NUVISAN’s Fragment Libraries
We offer two Ro3-compliant fragment libraries:
- 2,000 fragments in 50 mM D6-DMSO for biophysical screening
- 900 fragments in 500 mM DMSO for high-throughput X-ray (HTX) screening
A high purity level and an aqueous solubility of at least 1 mM of our fragments maximizes the chances of identifying high-quality fragment hits. Subsequently, fast structure–activity relationships (SAR) of fragment hits can be obtained either by SAR-by-catalogue at external vendors or by mining the internal life science database of more than 3 million compounds.
In addition to our in-house fragment libraries, we can also screen your fragment library. We can reformat your fragments to the plate format and stock concentration we require, depending on the needs of the individual biophysical method.
Fragment Screening Methods
We offer a wide range of biophysical methods to screen NUVISAN’s or your fragment library. Initially, we assess your target protein to identify the most appropriate biophysical screening method. We evaluate literature data and apply our long-time experience to choose the most appropriate fragment screening method(s) for your target.
Our fragment screening services include the following:
Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
Due to its low protein requirement and “label-free” methodology, SPR is one of the preferred biophysical methods for the screening of fragment libraries. Fragments are typically screened once at a given concentration for binding, and consequently, Kd titrations for all binders are performed. For more details about our SPR instruments and capabilities see SPR.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
NMR has evolved into a powerful technique in the field of fragment-based drug discovery. We offer protein-observed and ligand-observed methods, depending on your target needs. NMR is quite robust in detecting very weak interactions and can also be used to establish SARs. Furthermore, the binding sites of the fragment hits and their modes of action can be studied by NMR. More details about our NMR capabilities can be seen at NMR.
Thermal Shift Assay (TSA)
TSA measures the difference in the melting temperature of your target in the presence of a fragment. This method needs only a small amount of protein and is very fast. TSA can be used to identify tool fragments to validate other biophysical assays if no suitable tools are available early in the project. More about our TSA capabilities is at TSA.
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
As the primary screening method in fragment-based drug discovery, MS is often not used as a first choice, yet MS-based methods have the advantage of high sensitivity, low sample consumption, and being label-free. We offer MS-based screening for covalent libraries (LC-MS based), as well as so-called ligand-observed MS using fragment cocktails. Please find out more about our MS capabilities at MS.
High-Throughput X-ray Crystallographic Screening (HTX)
HTX fragment screening is a powerful technique for detecting and elucidating the binding mode of very weak binders. Our HTX workflow is fully integrated into our internal structural biology platform and allows for fast and efficient screening of up to 1,000 fragments.
Using our Echo Acoustic Liquid Handler, a large number of HTX fragments can be efficiently soaked into crystals, which are then prepared for data collection using our Shifter system. Visual Basic scripts allow for reliable data tracking throughout the complete workflow. Our continuous access to high-brilliance synchrotron sources, together with automated or manual data collection options, permits fast and reliable crystallographic data collection. Our in-house proprietary data analysis pipeline, including PanDDA, enables quick identification of datasets with a high likelihood of fragment binding, which are then refined and analyzed.
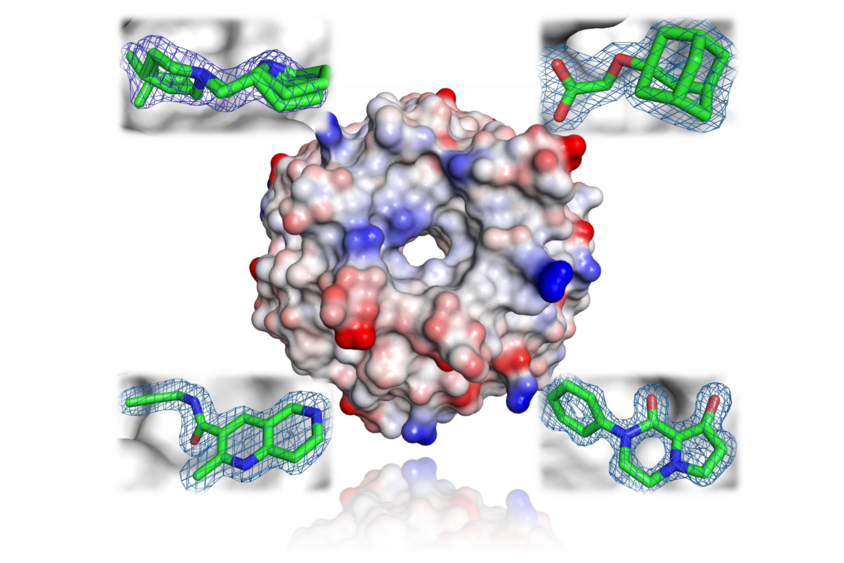
Example of X-ray Fragment Screen With E3 Ligase Subunit
E3 ligase subunit is a target with low druggability. We screened two libraries: 700 fragments of the Diamond fragment library resulted in 2 hits, and 200 fragments of the NUVISAN X-ray fragment library resulted in 8 hits. There were 6 hits bound to the pocket of interest, and the median resolution of the obtained structures was 1.75 Å.


