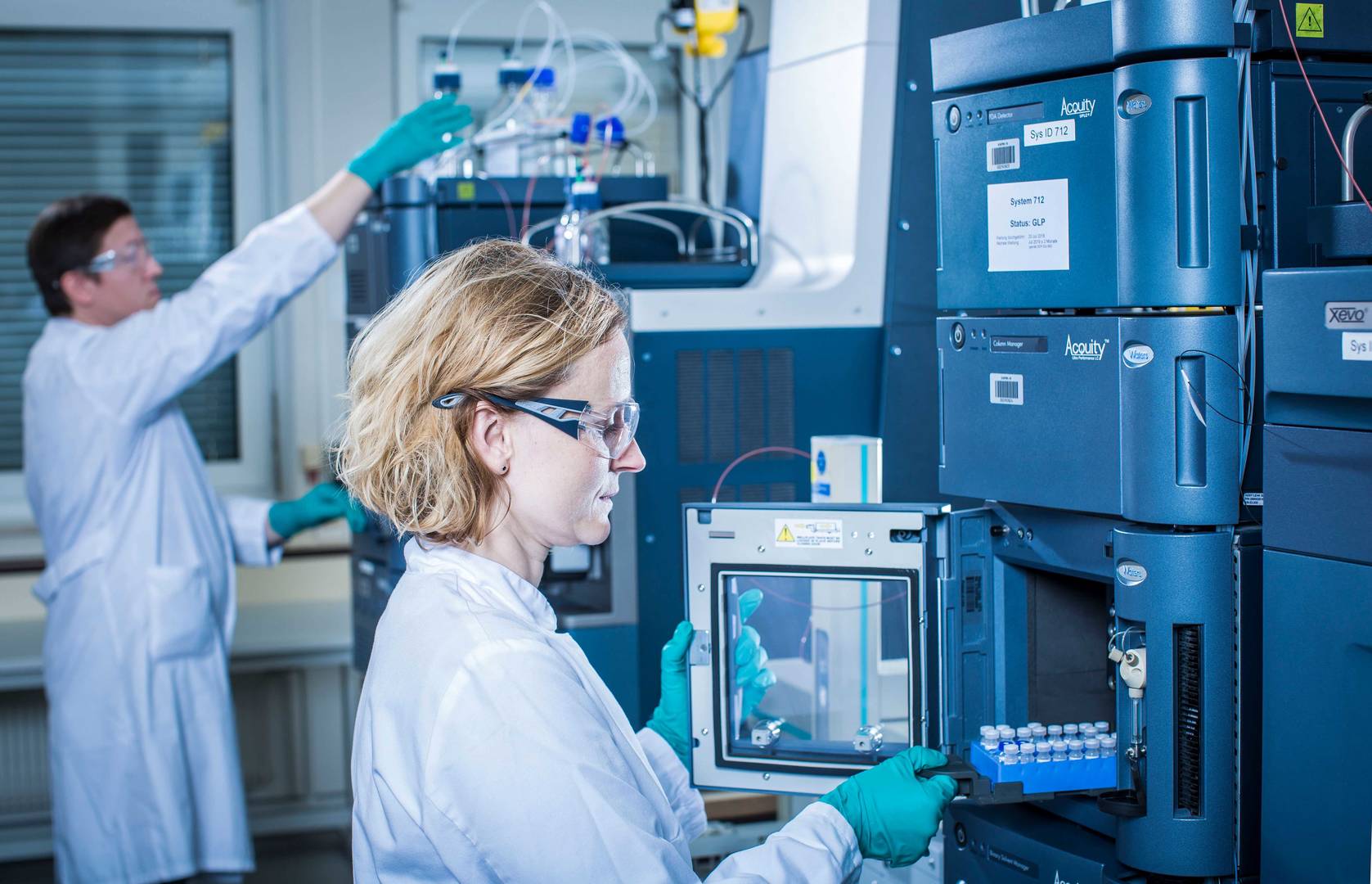




In vitro metabolism and plasma protein binding assays are essential for non-clinical safety evaluation and pharmacokinetic studies required before clinical trials. In vitro investigations of drug–drug interactions involving cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes and drug transporters are strongly recommended to guide participant selection, manage concomitant medications and define inclusion and exclusion criteria.
learn more
Understanding pharmacokinetics (PK) is crucial for the success of a drug candidate. PK data in rodent and non-rodent species are essential to determine if your compound has the appropriate properties for preclinical pharmacology (efficacy) and safety studies. Our in vivo PK study portfolio offers a wide variety of study designs across various animal species.
learn more
ADME studies in rodent and non-rodent species are important elements in non-clinical drug development. These studies investigate the disposition of unchanged drugs and total drug-related material, determining the metabolic fate of a drug. Such data are essential for assessing the safety and efficacy of drug candidates.
learn more
Radiolabelling drug candidates (e.g., 14C, 3H) is crucial in drug development, allowing for precise tracking and quantification of drug metabolism, distribution and elimination within the body. This technique provides valuable pharmacokinetic insights, helping provide insight into a drug's behaviour in different tissues, identify metabolites and assess potential toxicities. Stable isotope-labelled NCEs (D, 13C, 15N) are vital in bioanalysis as reference standards, offering a non-radioactive, consistent way to measure drug concentrations in biological samples.
learn more
Metabolism studies are integral to the development process, aiding in the safety and efficacy assessments of drug candidates. Investigating differences in metabolic profiles between humans and animal species used for toxicological testing early on is crucial to help identify unique and/or disproportionate human metabolites.
learn more
Our extensive, regulatory-grade in vitro and in vivo DMPK portfolio supports your IND package, helping ensure a smooth transition to the clinical stage. These efforts help identify potential safety concerns and estimate safe, efficacious starting doses for your clinical trials. We provide IND/IMPD-enabling assays, results and complete documentation in full compliance with international regulatory requirements.
learn more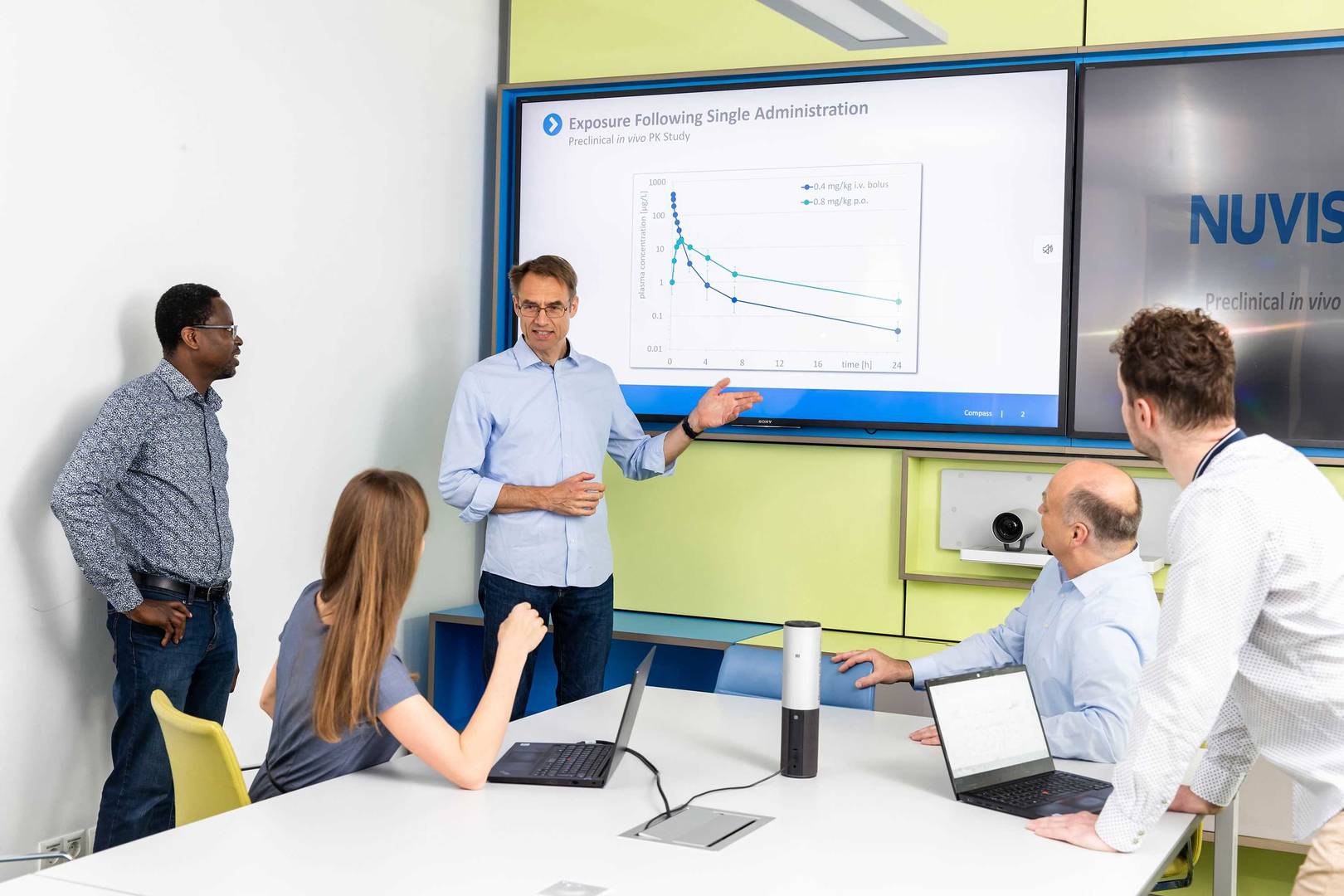
We help guide our pharmaceutical and biotech clients through all phases of the R&D value chain, from early drug discovery to clinical development and marketing authorisation. Our expertise lies in interpreting in vitro and in vivo DMPK data within the specific project context and identifying and overcoming DMPK-related development risks early.
learn more